ICASSP'2000 Tutorial
ICASSP'2000 Tutorial
Signal processing strategies in Neuroinformatics
Lars Kai Hansen
Department of Mathematical Modeling
Building 321
Technical University of Denmark
DK-2800 Lyngby, DENMARK
email: lkhansen@imm.dtu.dk
http://eivind.imm.dtu.dk
Abstract
This is the homepage for an
ICASSP'2000
tutorial on Neuroinformatics with specific emphasis on signal processing
aspects. Neuroinformatics is a new interdisciplinary research field which combines
``learning from the brain'' with ``learning about the brain''. This tutorial will focus on
signal processing strategies for neuroimaging, and includes discussions of
data preprocessing, data modeling by
clustering and neural networks, and information visualization by VRML (virtual
reality modeling language). A comprehensive Matlab toolbox for fMRI
signal processing including example neuroimaging datasets
is offered free of charge for scientific use.
Background
Neuroinformatics is a research field rooted in classical disciplines like
biology, physics, computer science, and engineering. Neuroinformatics combines
learning from the brain with learning about the brain. By studying
information processing in the brain neuroinformatics invents new engineering
paradigms (e.g. artificial neural networks) with the
grand but distant objective to understand the dynamics of the conscious mind.
Neuroinformatics is a key component of the US research program, the Human
Brain Project which is supported by major American governmental funding agencies.
The vast databases created by current brain scanning techniques calls for new innovative
signal processing strategies and for
for new visual and interactive means of communication and form
a significant engineering challenge for the next century. A point strongly
emphasized in Human Brain Project is the need for using the sc www for
communication and dissemination of results as well as information
infrastructure buildup.
Neuroinformatics
uses of multimedia techniques are now beginning to appear.
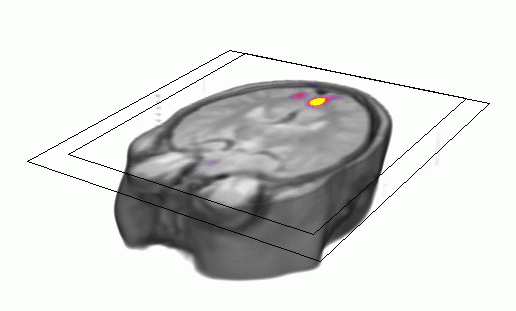
One of the major efforts in neuroinformatics concerns neuroimaging -- mapping brain
function by PET and fMRI (positron emission tomography and functional
magnetic resonance imaging).
Neuroimaging is opening a new window to the working human
brain and brain mapping will have immense influence on the way we think about the
brain both in research and in the clinic.
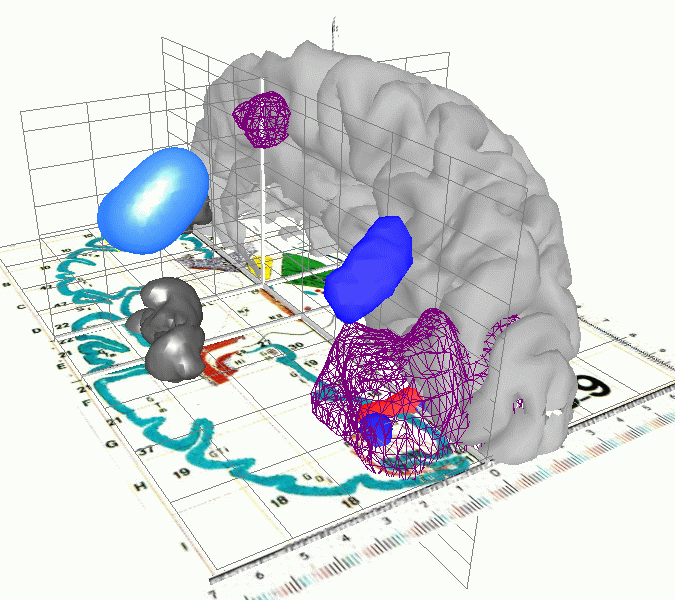
Adaptive systems and neural networks in particular construct abstract models by
learning. From an application point of view such knowledge gains credibility by
being expressed in intuitively accessible forms, say by computer graphics, and
interactively in the form of hypertext. With the advent of visual hypertexts such as
clickable maps or VRML (Virtual Reality Modeling Language) graphics and hypertext
are combined. The DTU-group has pioneered the use of VRML in neuroscience
contexts. The group's work can be accessed at
http://eivind.imm.dtu.dk/thor (group homepage)
http://hendrix.imm.dtu.dk (THOR center repository).
On the American site
http://neuroguide.com
the work is characterized as ``A glimpse
of the future. Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML) as applied to the human
brain, among other technical advances''.
Tutorial outline
The tutorial will review the basic neuroimaging data acquission schemes.
State the engineering challenges associated
with data analysis: normalization, intersubject co-registration by warping,
modeling using principal and independent component analysis
(PCA, ICA) an linear and non-linear representations, information
visualization and communication. The presentation will illustrated by
experimental data involving PET and fMRI studies of motor activity, visual
stimulation as well as cognitive tasks.
Neuroinformatics: definitions, background and major projects around the world
Neuroimaging: 3+1 D, the spatio-temporal structure of PET and fMRI data sets.
Signal processing challenges and current strategies for preprocessing
and representation: PCA, ICA.
The problem of extremely ill-posed learning (learning high-dimensional models from small databases).
Learning non-linear relations between blood flow and function
in the brain.
Information visualization: VRML
Perspectives and open research issues
Our group is offering a comprehensive Matlab toolbox for
fMRI
signal processing ``lyngby''. The toolbox is accompanied by example fMRI
data sets, offers an ideal introduction to the field,
and is offered free of charge for the scientific community.
Passcode for lyngby can be obtained by emailing lyngby@hendrix.imm.dtu.dk, the
documentation (postscript and html) can be accessed via our
software page
The presentation and the hand-outs will be based on the following
publications:
Benny Lautrup, Lars Kai Hansen, Ian Law, Niels Morch, Claus Svarer, and Stephen C. Strother:
"Massive Weight Sharing: A cure for Extremely Ill-posed Problems"
Workshop on Supercomputing in Brain Research: From Tomography to Neural Networks, HLRZ, November 21-23,
pp 137-144, (1994).
S.C. Strother, J.J. Sidtis, J.R. Anderson, L.K. Hansen, K. Schaper,
and D.A. Rottenberg: "15-O Water PET: More ``Noise'' than signal?"
In Quantification of Brain Function Using PET,
Eds R. Myers, V. Cunningham, D. Bailey, and T. Jones. Academic Press
Chapter 73, p 378-383, (1996).
S.C. Strother, N. Lange, J.R. Anderson, K.A. Schaper,
K. Rehm, L.K. Hansen, and D.A. Rottenberg:
"Activation pattern reproducibility: Measuring the effect
of group size and data analysis models".
Human Brain Mapping vol. 5, 321-316 (1997).
N. Morch, L.K. Hansen,
S.C. Strother, C. Svarer, D.A. Rottenberg, B. Lautrup,
R. Savoy, O.B. Paulson:
"Nonlinear versus Linear Models in Functional Neuroimaging:
Learning Curves and Generalization Crossover".
Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on
Information Processing in Medical Imaging, 1997,
Eds. J. Duncan and G. Gindi. Lecture Notes in Computer
Science vol. 1230, Springer Verlag 259-270, (1997).
F.AA. Nielsen and L.K. Hansen.
"Interactive Information Visualization in Neuroimaging".
NPIVM'97 - Workshop on New Paradigms in Information Visualization
and Manipulation. David S. Ebert, Charles K. Nicholas (eds.)
ACM ISBN 1-58113-051-1. (1997)
L.K. Hansen, N. Morch, and F.AA. Nielsen:
"Neural Net in Functional Neuroimaging". Tutorial Paper
for NORSIG'98. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nordic Signal Processing
Symposium, Vigso, Denmark 1998. Eds. P. Dalsgaard and
S.H. Jensen, pp. 1-8, (1998).
C. Goutte, P. Toft, E. Rostrup, F.AA. Nielsen and L.K. Hansen:
"On clustering fMRI time series". NeuroImage vol. 9:298-310, (1999).
L.K. Hansen, J. Larsen,
F.AA. Nielsen, S.C. Strother, E. Rostrup,
R. Savoy, N. Lange, J.J. Sidtis, C. Svarer,
O.B. Paulson: "Generalizable Patterns in Neuroimaging:
How Many Principal Components?" NeuroImage vol. 9, 534-544 (1999).
U. Kjems, S.C. Strother, J. Anderson, I. Law, L.K. Hansen.
"Enhancing the Multivariate Signal of
15-0 water PET Studies With a New Non-Linear
Neuroanatomical Registration Algorithm".
IEEE Transactions in Medical Imaging vol. 18 306-319, (1999)
N. Lange, S.C. Strother,
J.R. Anderson, F.AA. Nielsen, A.P.
Holmes, T. Kolenda, R. Savoy, L.K. Hansen.
"Plurality and Resemblance in fMRI Data Analysis"
NeuroImage, vol. 10 (3):282-303, (1999)
Links to neurosites
NIMH Neuroinformatics home
Human Brain Project
 International Neuroimaging Consortium
Rottenberg groups homepage.
6'th Int. Conf on Functional Mapping
of the Human Brain (San Antonio, June 2000).
Keith Worsley's
homepage (statistical analysis).
Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) home
Roger Woods' AIR co-registration
software
Ulrik Kjems'
3D non-linear Warp toolbox (UNIX)
International Neuroimaging Consortium
Rottenberg groups homepage.
6'th Int. Conf on Functional Mapping
of the Human Brain (San Antonio, June 2000).
Keith Worsley's
homepage (statistical analysis).
Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) home
Roger Woods' AIR co-registration
software
Ulrik Kjems'
3D non-linear Warp toolbox (UNIX)
Return to homepage.



